
Businesses Worldwide Embrace Sustainability in Response to EU CSDDD and Other ESG Legislation
In 2023, businesses are taking sustainability more seriously due to the passage of ESG legislation like Germany's Supply Chain Act and the EU's Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD). This shift isn't confined to European companies alone; globally, nearly half of companies are directly or indirectly impacted by ESG legislation, and are taking steps to improve ESG compliance.
These regulations are causing a ripple effect, prompting even businesses outside the scope of ESG legislation to place greater emphasis on environmental responsibility, fair labor practices, and responsible sourcing. As supply chains adapt to align with these ESG values, companies must swiftly adjust to maintain their competitiveness, adhere to relevant regulations, and meet the evolving demands of both customers and stakeholders.
How ESG Legislation Is Impacting Global Supply Chains: EU CSDDD, Germany’s Supply Chain Act, and More
Businesses worldwide are rapidly increasing their focus on sustainability in 2023 as regulations like Germany's Supply Chain Act and the EU's CSDDD take effect. These regulations are having a “trickle-down effect,” in which even businesses that are not directly impacted by these regulations are paying more attention to ESG practices.
Around 47% of businesses QIMA surveyed around the world stated that they are directly or indirectly affected by ESG legislation. In the EU, this number is even higher, with 63% of businesses directly or indirectly affected by ESG legislation, and only 23% of businesses not impacted at all.
The percentage of US businesses directly under the scope of ESG legislation is higher than in the EU (39% in the US vs 21% in the EU). This may be because ESG-related legislation has been in place longer in the US, such as the Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502, passed in 2010. However, when you take both indirectly and directly impacted companies into account, fewer businesses in the US say they’re impacted by ESG legislation than in the EU.
Asia has the lowest percentage of businesses reporting direct or indirect impacts from ESG legislation, at 44%. This is likely due to lower levels of ESG regulatory adoption and enforcement across Asian countries, as well as differing stages of awareness and preparedness within the region. While the significance of ESG issues is growing globally, the extent to which it affects businesses can differ based on regional regulatory landscapes and market dynamics.
Fig. 1. “Does your business fall into the scope of any ESG legislation?” (grouped regionally by respondent headquarters location)
Globally, almost half of the businesses QIMA surveyed are either directly or indirectly impacted by ESG legislation. In the EU, this number is even higher, with 63% of companies headquartered in the EU directly or indirectly falling into the scope of ESG legislation.

ESG Legislation Leads to Increased Focus on Supplier Compliance
Globally, over half of businesses (55%) are voluntarily giving more weight to supplier compliance when making sourcing decisions, even if not legally required to do so. Supplier compliance is increasingly recognized as a crucial element in businesses' commitment to responsible and sustainable practices. This change shows that businesses are determined to make sourcing choices that match environmental and social responsibilities, reflecting the growing influence of ESG legislation across global supply chains.
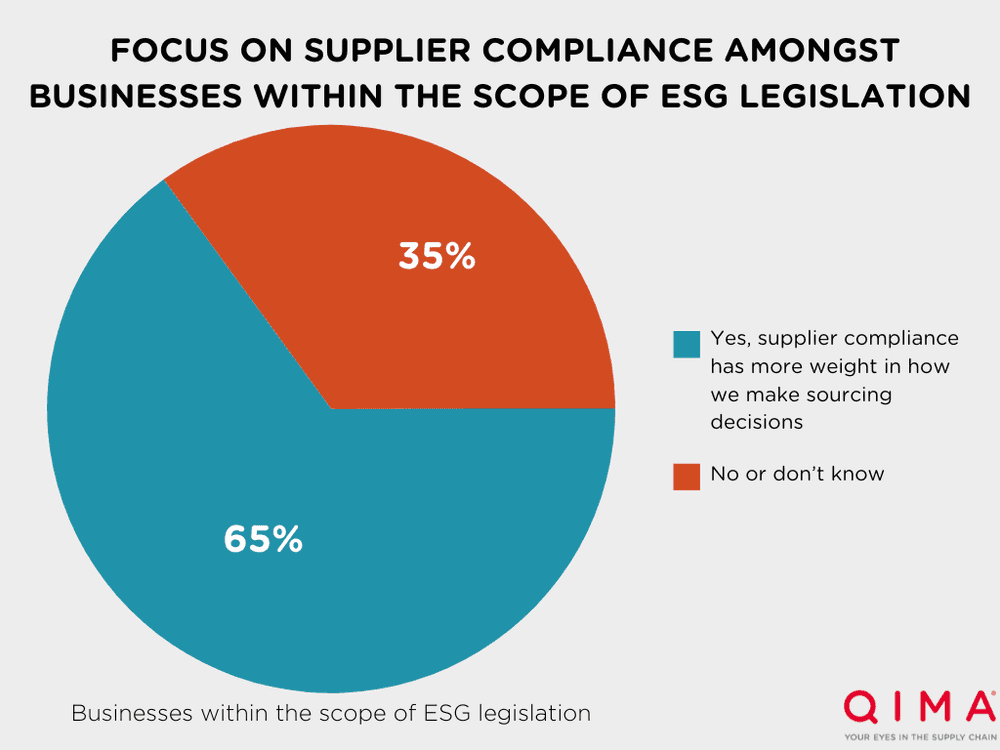
Among businesses that are directly within the scope of ESG legislation, even more attention is being paid to supplier compliance. 65% of businesses directly impacted by ESG legislation say supplier compliance has a stronger impact on their sourcing decisions in 2023 than in 2022.
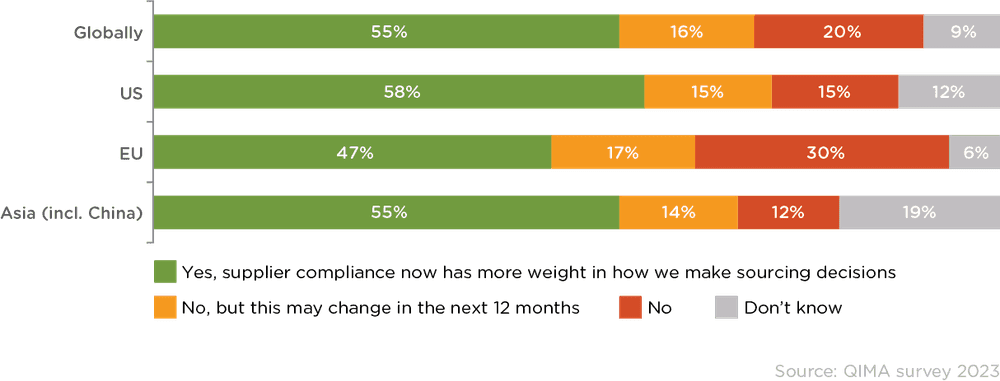
The US leads the trend, with 58% of US businesses placing a stronger focus on supplier compliance than in the past.
While Asia-based businesses report being least impacted by ESG regulations, a higher percentage of Asian companies are placing more weight on supplier compliance in their sourcing decisions than in the EU (55% in Asia vs. 47% in the EU). This shows that there may be other driving forces behind the increased focus on supplier compliance than compliance with ESG legislation. For example, Asian businesses might be responding to heightened global scrutiny and growing consumer demands for ethical and sustainable sourcing practices, which are not solely driven by legal mandates but by a broader shift in market expectations.
Focus on supplier compliance also varies by industry. Sectors with a recent history of strong public scrutiny, such as Textile and Apparel, tend to have the highest percentage of businesses paying closer attention to supplier conduct compared to 2022. Other industries with a stronger focus on supplier compliance in 2023 include promotional products, food, and footwear. The industry with the least growth in focus on supplier compliance when it comes to sourcing decisions is the toy and recreational products industry.
Fig. 2. “Does supplier compliance have a stronger impact on your sourcing decisions now compared to 12 months ago?” (grouped by respondent HQ location, regardless of whether respondent is within the scope of ESG legislation)
Compared to one year ago, more than half of companies surveyed say supplier compliance has a stronger impact on their sourcing decisions. In the US, supplier compliance is gaining traction as a driver of sourcing decisions for 58% of companies.
Key Figures
QIMA’s H1 survey of more than 250 businesses shows that:
1. Global increase in focus on supplier compliance: More than half (55%) of businesses are voluntarily giving more weight to supplier compliance when making sourcing decisions compared to one year ago, even if not legally required to do so.
2. Businesses within the scope of ESG legislation give more weight to supplier compliance: 65% of businesses within the scope of new ESG regulations like the EU's CSDDD are focusing more on supplier compliance in their sourcing decisions.
Fig. 3. “Does supplier compliance have a stronger impact on your sourcing decisions now compared to 12 months ago?” (among businesses directly within the scope of ESG legislation)
3. Increased public scrutiny leads to closer attention to supplier compliance: Sectors with a recent history of strong public scrutiny, such as Textile and Apparel, tend to have the highest percentage of businesses paying closer attention to supplier conduct.
Read the full report: Q3 2023 Barometer
Related Articles


